March 31, 2025, 8:57 am | Read time: 6 minutes
Heartworms (Dirofilaria immitis) are parasitic roundworms that infest the heart and lungs of dogs. The disease caused by these parasites is called dirofilariasis. It is one of the most serious and life-threatening parasitic diseases in dogs. And it can also be dangerous for humans.
Heartworms, transmitted by mosquitoes, typically reside in dogs’ hearts and the vessels leading from the heart to the lungs. An untreated heartworm infestation is life-threatening for affected dogs and also poses a significant health risk to humans. However, according to veterinarian Dr. Vanessa Herder in an interview with PETBOOK, “Dogs are the only mammal species that are frequently infected with heartworm.”
Heartworms Are Also Spreading More and More in Central Europe
“In regions where this disease is common in dogs, other animals such as cats, foxes, wolves, ferrets, horses and, rarely, humans can also be affected.” Heartworm incidents are particularly common in Asia, Australia, and North and South America. But not only there. Many southern European countries such as Italy and Spain are also affected, says the vet. The risk is increasing domestically as well. “The disease is currently also spreading in northern countries.” Cases of transmission have also been documented in Germany.
Dogs and foxes are particularly susceptible to infection. On average, infections in these animals are ten times more common than in cats.1 Heartworms are transmitted by mosquitoes. The first larval stages of the heartworms (microfilariae) live in the blood of their final hosts and are ingested by the mosquitoes during the blood meal.
Heartworms Can Grow up to 20-30 cm Long
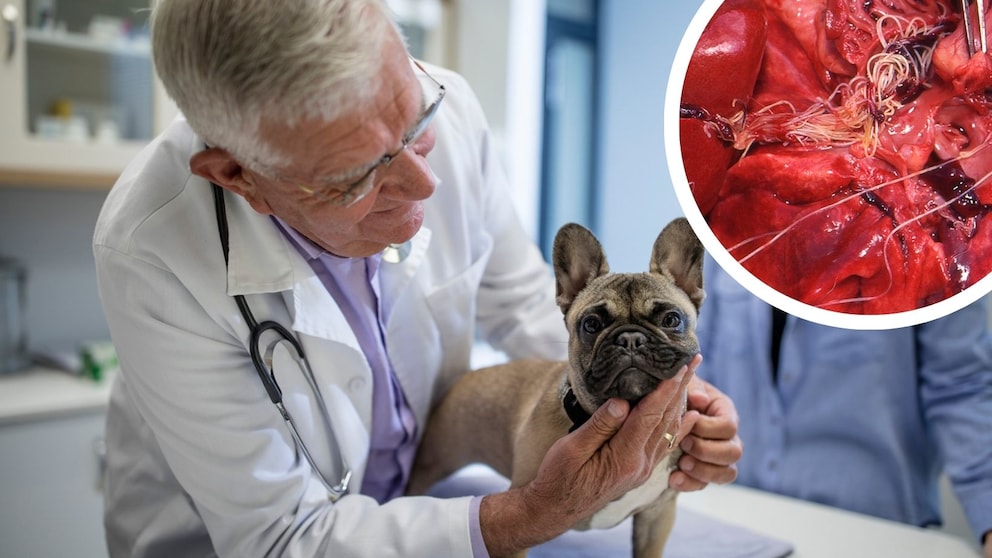
In the mosquito’s body, the microfilariae develop into infectious larval stages that are transferred to a new host during the mosquito’s subsequent bite. After migrating through the connective tissue, they reach the bloodstream and enter the heart or the large blood vessels of the lungs. “The adult worm is found in pulmonary arteries and in the right heart — it can also occur in other blood vessels. Unusual localizations are the eye and the brain,” explains Dr. Herder.
The worms can reach a length of up to 20-30 cm and a diameter of 0.7 to 1.3 cm. “The female worms give birth to the microfilariae in the bloodstream, and mosquitoes are part of the development cycle. Infection of the animal or human occurs via the bite of the mosquito.” Parasite development takes around seven months, and adult worms can live for several years, according to the expert.
Heartworm Infestation Often Remains Undetected for a Long Time
Particularly insidious: the symptoms of a heartworm infestation in dogs can remain undetected for a long time, with devastating consequences! “The clinical signs of dirofilariasis are cardiovascular diseases that manifest themselves as coughing and exhaustion with heart failure.” Infected dogs are usually more than five years old and have already been infected several times, explains Dr. Vanessa Herder.
“If there are more than 50 worms per animal, clinical symptoms usually occur. In cats, the clinical picture often presents with coughing, breathing difficulties, vomiting, and neurological signs. Occasionally, sudden death can occur.” Owners should, therefore, take their pet to a vet as soon as possible if there is a suspicion of infection and the animal has been in one of the affected regions in recent months.
Owners should also take a very close look when introducing dogs from southern European animal welfare organizations and consult a vet if there are any indications or suspicions. However, heartworm infestation is a serious risk not only for animals but also for humans.2
Heartworms Can Be Life-Threatening for Humans
“Dirofilariasis in humans is a life-threatening disease if the lungs are affected and the disease is not diagnosed correctly.” In addition to high blood pressure, all animals can also suffer severe blood vessel damage, explains the vet in an interview with PETBOOK. “Macrocyclic lactones are used as a therapy, although it should be noted that some worms have developed a resistance to this medication.”
This is why some countries, such as Italy, have special programs in place to curb further spread. The “One Health” initiative in Italy is trying to ensure that animals and humans remain free from infection. However, experts warn that we should not panic here either. Even though heartworms pose a serious risk, they are not transmissible from infected dogs to animals or humans and are generally curable. However, the cure depends heavily on the stage of the disease, the individual constitution of the dog, and the quality of veterinary treatment.
Heartworm Treatment Is Lengthy and Not Without Risk!
Heartworm disease is serious; treatment is lengthy and not without risk — but it can be successful. As a rule, at least four to six months of treatment is to be expected — longer depending on the severity. It is, therefore, important to detect the infestation as early as possible. As with most diseases, this also applies here: The earlier it is detected, the better the chances of recovery. Treatment should always be supervised by a vet who is familiar with heartworm infestation or is prepared to deal with this issue.
In the United States, heartworms are not necessarily a common daily diagnosis for veterinarians. There are also various risks that can occur during treatment. In some cases, dying worms can lead to a pulmonary embolism. With a high worm burden, inflammatory reactions, or, in cases of doubt, even long-term damage to the heart and lungs can occur.
What Is the Course of Treatment?
- Stabilization of the dog (in case of symptoms such as heart failure)
- Killing the microfilariae (e.g., with ivermectin or moxidectin)
- Killing the adult heartworms with the active ingredient melarsomine
- Strict resting phase of several weeks — dying worms can clog vessels → danger to life!
- If necessary, supportive medication (anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics such as doxycycline against Wolbachia bacteria)
Even after successful deworming, permanent damage to the heart, lungs, or blood vessels can remain, especially if the disease is detected late. However, many dogs recover completely and can lead a normal life after treatment.
Triggers of diarrhea Giardia in dogs — symptoms, causes, and treatment

Parasites Recognizing and Treating Lungworm Infestation in Cats

Zoonoses Feline zoonoses: Cats can transmit these diseases to humans
Can Preventative Measures Be Taken?
As heartworms are transmitted by mosquitoes, prophylaxis is particularly important, especially when traveling to risk areas. Therefore, it is recommended that you administer antiparasitic medication regularly to your traveling canine companion. In addition, mosquito repellents should be used in the form of spot-on preparations, collars, or environmental repellents. If you have any questions, owners can seek advice from their trusted vet.3